
SHINKO ELECTRIC INDUSTRIES CO., LTD.

SHINKO ELECTRIC INDUSTRIES CO., LTD.
 Climate Change
Climate Change
The Shinko Group is engaged in a variety of activities to fulfill the responsibility of a manufacturing company to reduce environmental impact. Among these, the greatest priority is given to responding to climate change, based on our understanding that it is essential for realizing a sustainable society, and related activities are conducted throughout the company.
International frameworks such as the Paris Agreement, together with the strengthening of global regulations and expanded application of carbon taxes, are accelerating the trend toward decarbonization in many countries throughout the world. The Shinko Group is working to respond to climate change by clarifying its goals in accordance with its Environmental Policy and Environmental Vision 2050 and by setting medium- to long-term environmental targets. We are strengthening our activities to achieve carbon neutrality as soon as possible and contribute to the realization of a decarbonized society.

The Financial Stability Board (FSB) has established the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) to reduce the risk of instability related to climate change in financial markets. Responding to the TCFD recommendations in 2017, the Shinko Group has committed to making disclosures in line with the recommendations, and as SHINKO ELECTRIC INDUSTRIES CO., LTD., we expressed our support for the TCFD recommendations in May 2022.
The Shinko Group actively discloses information on climate change to various stakeholders.
Shinko has established the Environmental Committee chaired by the Representative Director of Board, President, and the Environmental Measures Execution Committee as a subordinate organization under the Committee, as a framework for promoting environmental management. Furthermore, at each of our plants in Japan and SHINKO R&D Center, we have established Green Factory Promotion Subcommittees consisting of manufacturing divisions and related divisions to implement specific climate change measures, including the promotion of energy conservation and the introduction of high-efficiency equipment in manufacturing processes and plant utility equipment.
Our overseas manufacturing subsidiaries are also working to reduce their environmental impact, including climate change, under their own sustainability promotion systems.
The Risk Management Committee, chaired by the Representative Director of Board, President, has been established as a company-wide risk management system, including responses to climate change risk, to promote risk management for the entire group. To fully understand and respond to risks that could impact our business operations, including climate change, we analyze and respond to risks Groupwide.

Evaluation of the Importance of Risks and Opportunities
In initiating scenario analysis, the Shinko Group identifies the risks and opportunities arising from climate change that it faces, define the target period, and evaluate importance based on the magnitude of qualitative impacts on its business.
Please refer to Sustainability Report 2025 (Climate Change Strategy, p. 31) for the Evaluation of the Importance.
Defining Scenario Groups
Based on the sixth assessment report released by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), the Shinko Group has established a "2°C or lower scenario" and a "4°C scenario." We are using external information such as the International Energy Agency's (IEA) STEPS (Stated Policies Scenario), APS (Announced Pledges Scenario), and NZE (Net Zero Emissions by 2050 Scenario) as references up to the year 2050.
In the 2°C or lower scenario, we expect tighter regulations, such as the introduction of a carbon tax, and the risk of higher prices for electricity and raw materials like metal. We also expect opportunities in the form of increased sales of low-carbon, energy-saving products thanks to efficiency improvements in manufacturing facilities achieved by meeting the decarbonization needs of markets and customers, and stabilization of costs associated with the creation of renewable energy. Under the 4°C scenario, physical risks are projected to be greater than under the 2°C or lower scenario. This is due to the intensification of disasters caused by extreme weather, leading to increased frequency and scale of disasters such as wind and water damage and floods.
Business impact assessment
Based on the scenario analysis, the business impact assessment of transition risk in the 2°C or lower scenario is as follows.
In the below 2°C scenario, the financial impact of the introduction of a carbon price in 2050 is significant.
Based on these results, we will take measures to respond to future risks.
The 4°C scenario and other risks and opportunities will be evaluated in the future.
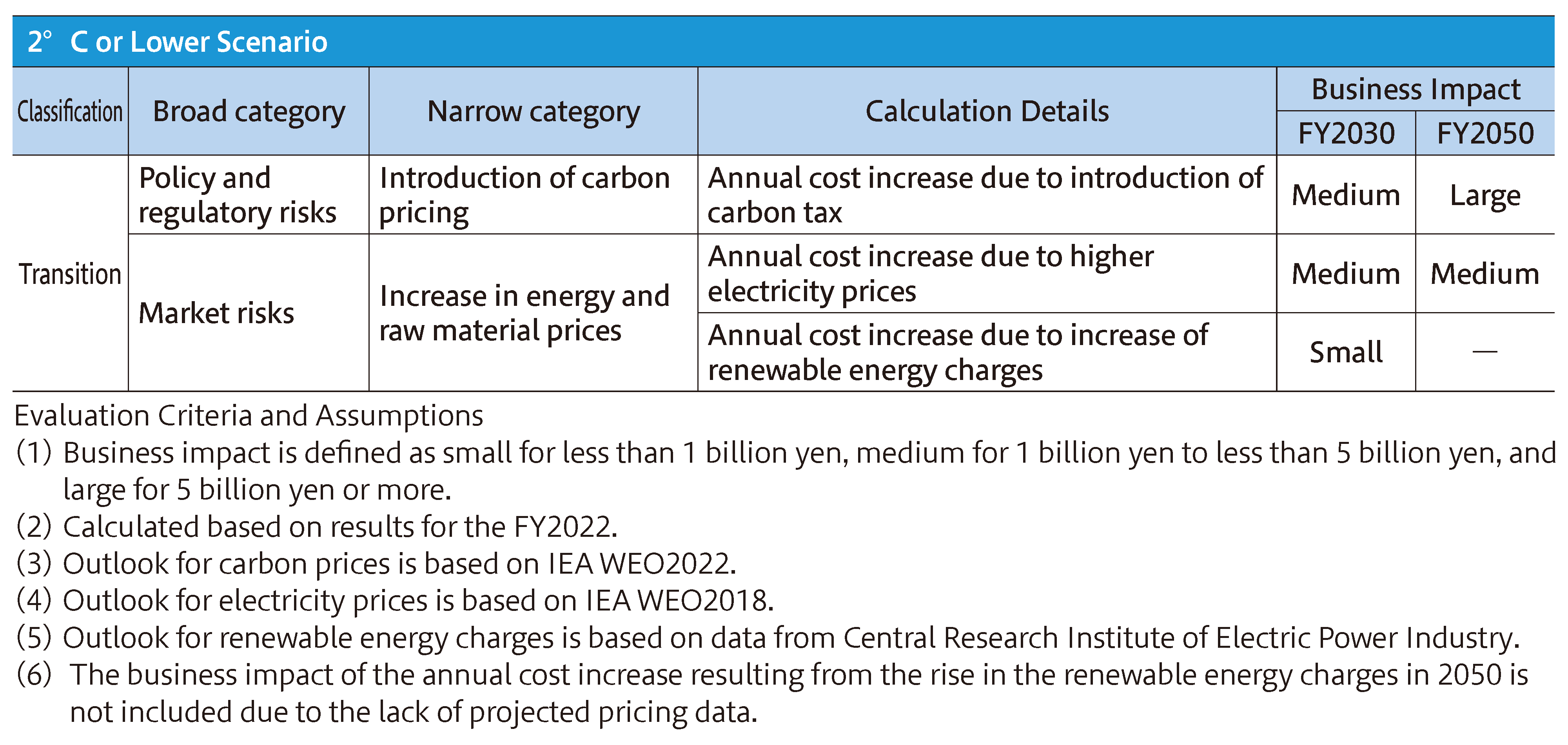
Countermeasures and Transition Plans
For risks expected to have a significant business impact, we are reviewing countermeasures and transition plans such as the following.
We will review and update them regularly, considering scientific progress, changes in laws and regulations, etc.
Risk Management Process
To fully understand and respond to risks that could affect the business operations of the Shinko Group, including climate change, we identify, assess, and manage risks across the Group. In order to conduct regular company-wide risk assessments, each division and group company conduct assessments on risk threats, such as the impact and likelihood of the occurrence of risks, and the status of countermeasures. For the risks related to climate change, we use information collected from across the Group to assess policies, reputation, natural disasters, the supply chain, products and services, etc. The results of the assessments, answered by each division, are conducted using a centralized matrix analysis to investigate the possible impact and likelihood of occurrence, then high-priority risks are identified at the company-wide level. Also, the Environmental Committee shares business risks, opportunities, and countermeasures related to climate change and manages the progress of countermeasures. In addition, the Shinko Group has established an environmental management system based on ISO 14001. Under this system, we monitor risks on compliance, etc.
Adaptation to Climate Changes
As part of our efforts to adapt to climate change, we are strengthening our internal countermeasures to reflect the increasing severity and frequency of typhoons and floods caused by extreme weather events. Specifically, in addition to taking preliminary measures based on hazard maps and other information at each site, we are working to minimize damage by establishing a "Typhoon and Flood Damage Timeline" for each site and division that defines action criteria and outlines of actions to take in the event of a disaster, and by conducting training on an ongoing basis.
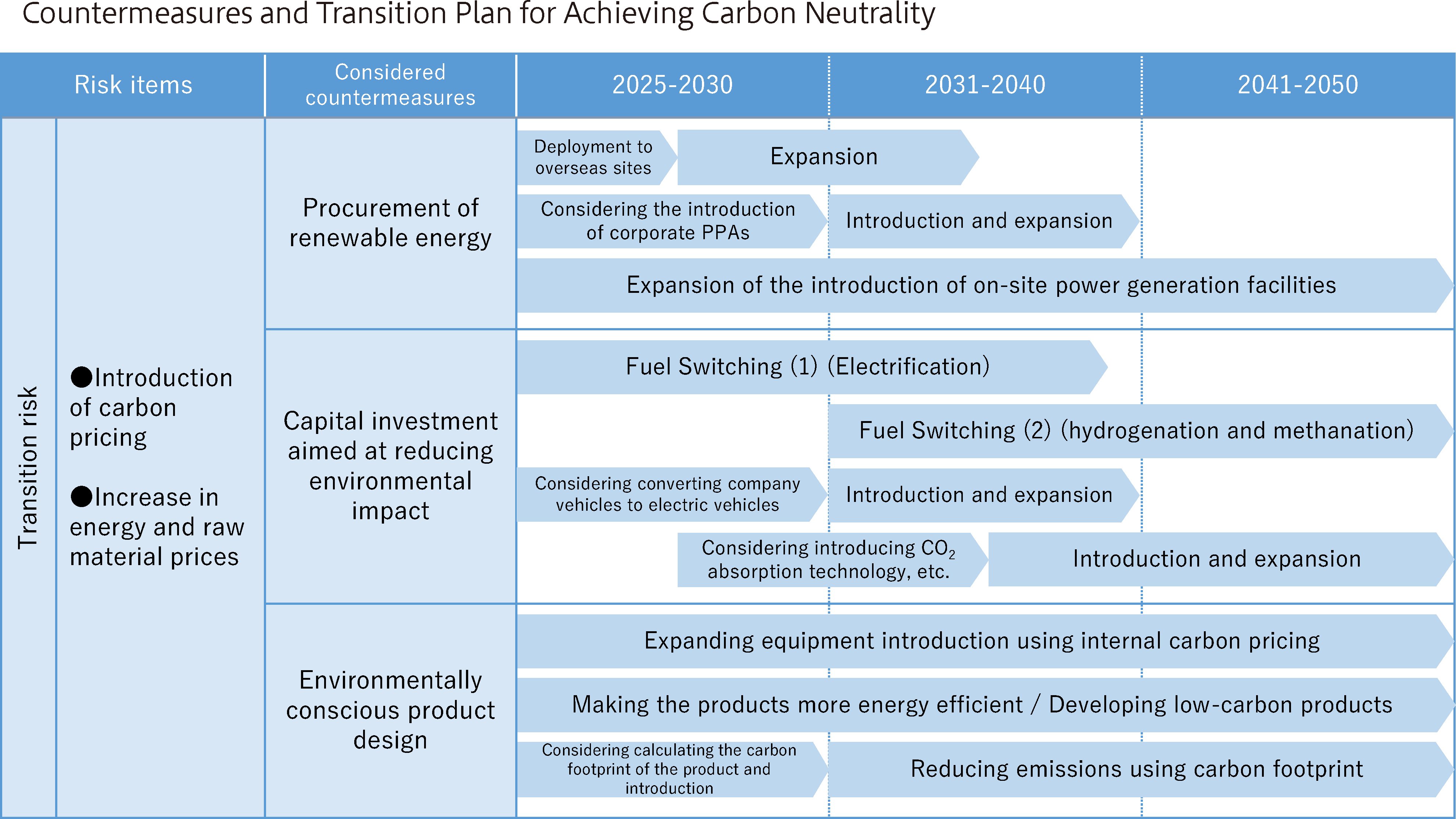
The Shinko Group, recognizing the importance of reducing greenhouse gas emissions and adopting renewable energy for countering climate-related risks, uses greenhouse gas emissions and renewable energy adoption rates as key metrics. With regard to the reduction of net greenhouse gas emissions, we aim to achieve carbon neutrality with net-zero emissions by FY2050. Backcasting from that, we have established a target for FY2030 and are conducting activities to help us meet it. In the area of renewable energy utilization, we have set a target of 100% utilization by FY2030 and are working toward that target. We have also set annual targets in the “Environmental Action Program (Stage 11)” which serves as the short-term targets for achieving the “Medium- to Long-Term Environmental Targets”, and are monitoring metrics to manage the progress of our strategy and associated risks.
Note: Boundary of the targets is Scope 1 and Scope 2 at all business sites in Japan.
Targets・Results
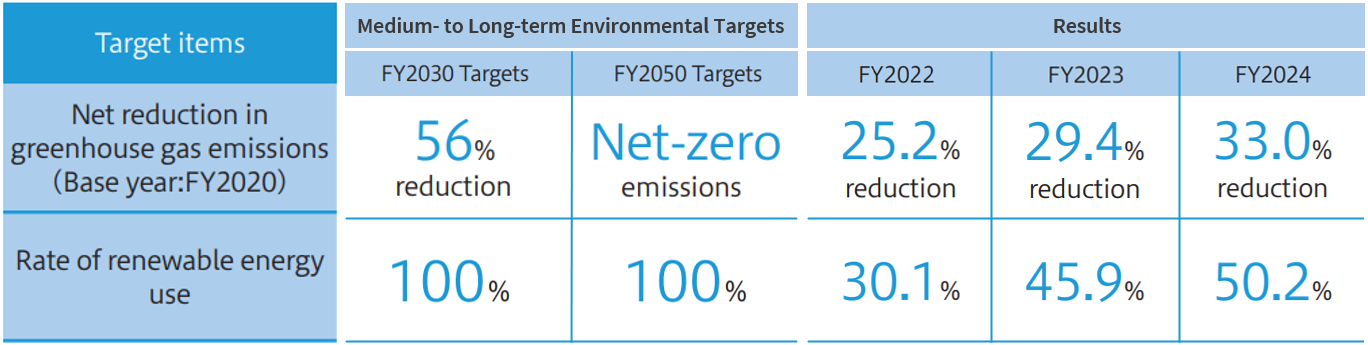
Net reduction rate of greenhouse gas emissions
Rate of renewable energy use
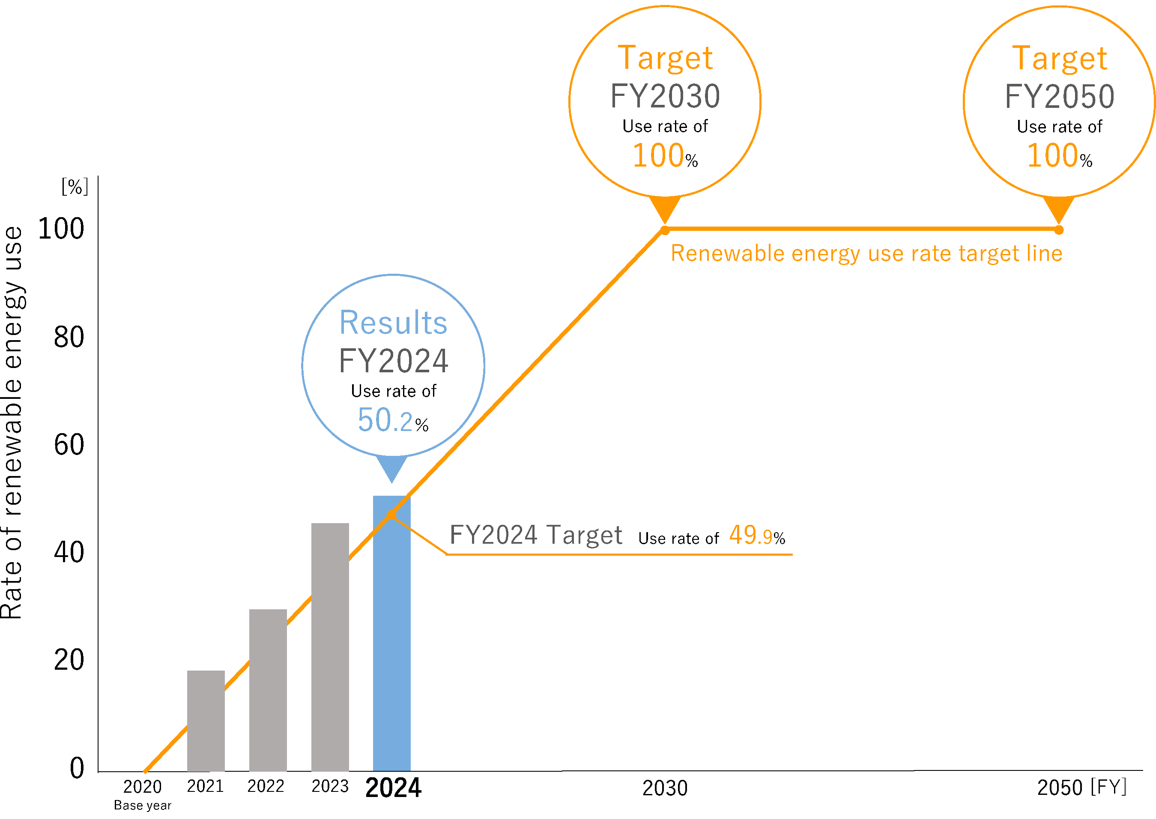
For details, please refer to Sustainability Report 2025 (Climate Change Metrics and Targets, p. 34-35).
At plants in Japan and SHINKO R&D Center, the Green Factory Promotion Subcommittee, in which manufacturing divisions, facilities management divisions, and related divisions participate, is central to promoting the reduction of CO2 emissions through energy conservation and energy efficiency improvements in manufacturing and utility facilities. Furthermore, by implementing various measures, including consolidation of equipment, reduction of standby power, and the switch to LED lighting, we are strengthening company-wide efforts to realize low-carbon manufacturing processes and facilities through efficient energy use.
In addition, we have introduced the concept of internal carbon pricing (ICP)*, which converts CO2 emissions from capital investments into monetary amounts and uses them as a basis for making investment decisions, and we are using it to reduce CO2 emissions.
Although energy consumption is expected to increase in the future due to the construction of a new plant and buildings and the expansion of production facilities in line with the strengthening of the production system, we will further strengthen various measures to reduce CO2 emissions.
* Internal Carbon Pricing (ICP): A mechanism whereby companies set their own price for CO2 emissions and use it to make investment decisions
Examples of Activities
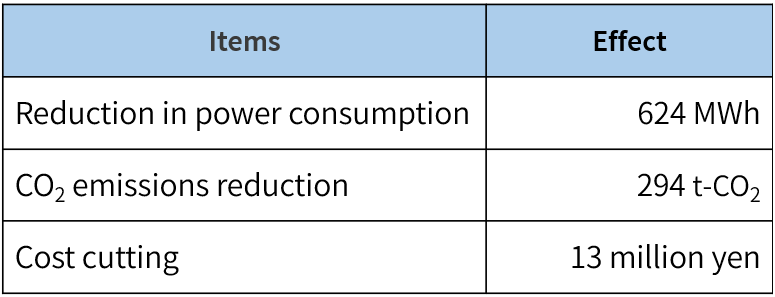
Arai Plant (Myoko City, Niigata Prefecture) has focused on cleaning equipment within manufacturing processes that consume relatively large amounts of energy. By implementing energy-saving measures—such as temporarily halting conveyors, showers, heaters, and air knives during standby time—and optimizing operating conditions, the plant has significantly reduced energy consumption, leading to lower CO2 emissions and cost savings.
Effect of Cleaning Equipment Measures(FY2024)
CO2 from electricity purchased from external sources accounts for a large proportion of the CO2 emitted in the course of the Shinko Group's business activities. We have been installing photovoltaic power generation equipment at our business sites to expand the use of renewable energy.
The amount of electricity generated by solar power generation facilities in FY2024 was 692 MWh. At the same time, CO2 emissions were reduced by approximately 290 t-CO2.
We are also working to expand the use of renewable energy through the purchase of CO2-free electricity from power companies and the utilization of non-fossil certificates, contributing to higher renewable energy usage rates.
The procurement of renewable energy through the purchase of CO2-free electricity and the use of non-fossil certificates in FY2024 amounted to 174,515 MWh, resulting in a reduction of approximately 73,000 t-CO2 in CO2 emissions.
Aiming to achieve a 100% renewable energy use rate, we will continue to focus on the creation and increased use of renewable energy by expanding the installation of solar power generation facilities at existing plants and newly constructed plants/buildings, as well as by purchasing CO2-free electricity and utilizing non-fossil certificates.
We will continue to contribute to the achievement of carbon neutrality and the realization of a decarbonized society by strengthening and accelerating various company-wide initiatives.