
SHINKO ELECTRIC INDUSTRIES CO., LTD.

SHINKO ELECTRIC INDUSTRIES CO., LTD.
To promote environmental management, the Shinko Group has established an environmental management system based on the international standard ISO 14001 as a framework for balancing business activities with social needs and environmental issues. Through the PDCA cycle in accordance with our environmental management system, we strive for continuous improvement and betterment of our environmental performance.
Shinko Group in Japan has made environmental protection a top management priority and are engaged in environmental preservation activities based on a promotion system established in accordance with the Shinko Way, the basic philosophy of the Shinko Group.
Environmental Activity Promotion System
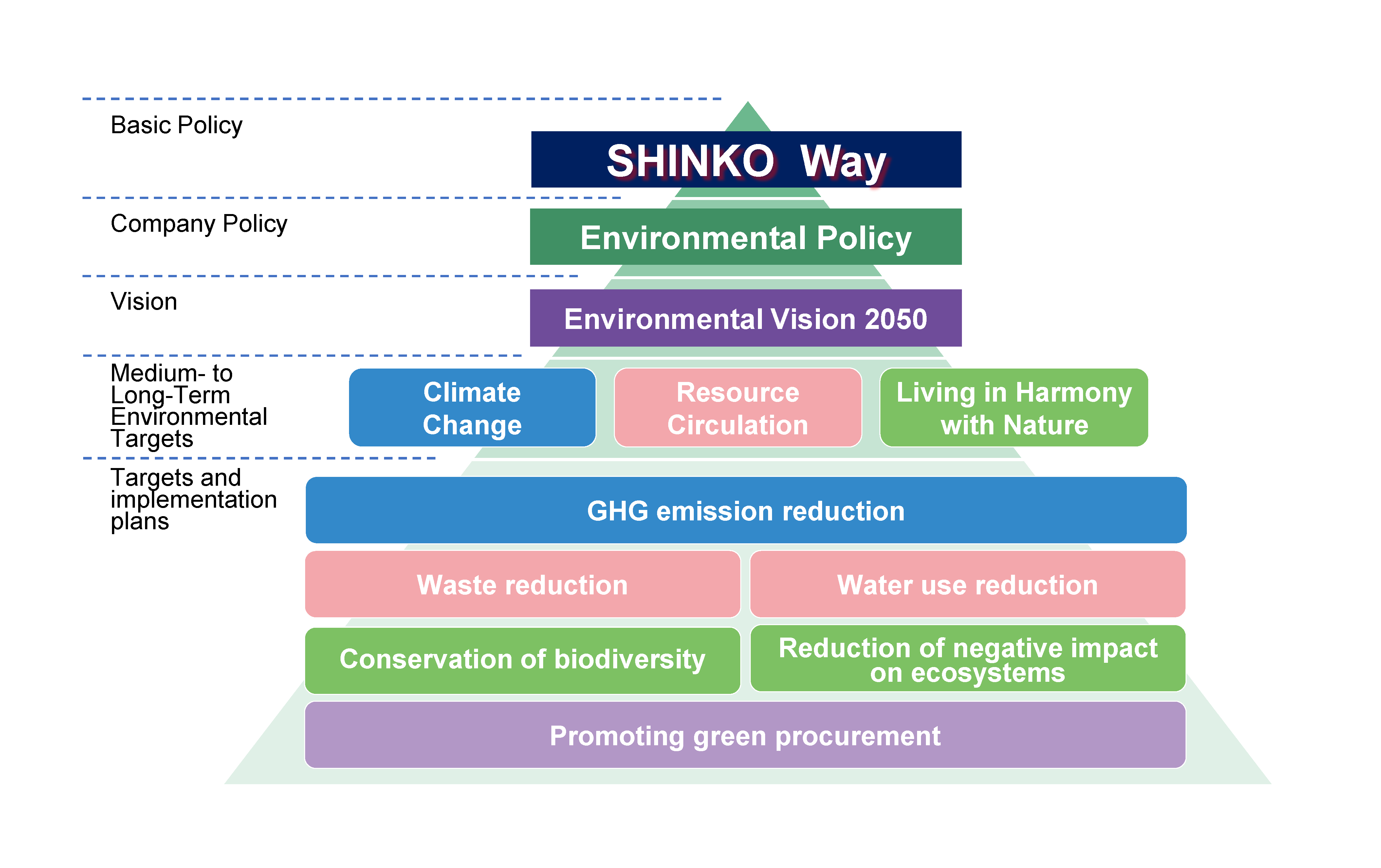
We outlined our environmental commitment in the Environmental Policy, and, to fulfill this commitment, we have articulated our approach and goals in our Environmental Vision 2050, and set "Environmental Targets (medium- to long-term environmental targets and Environmental Action Program)" to achieve them.
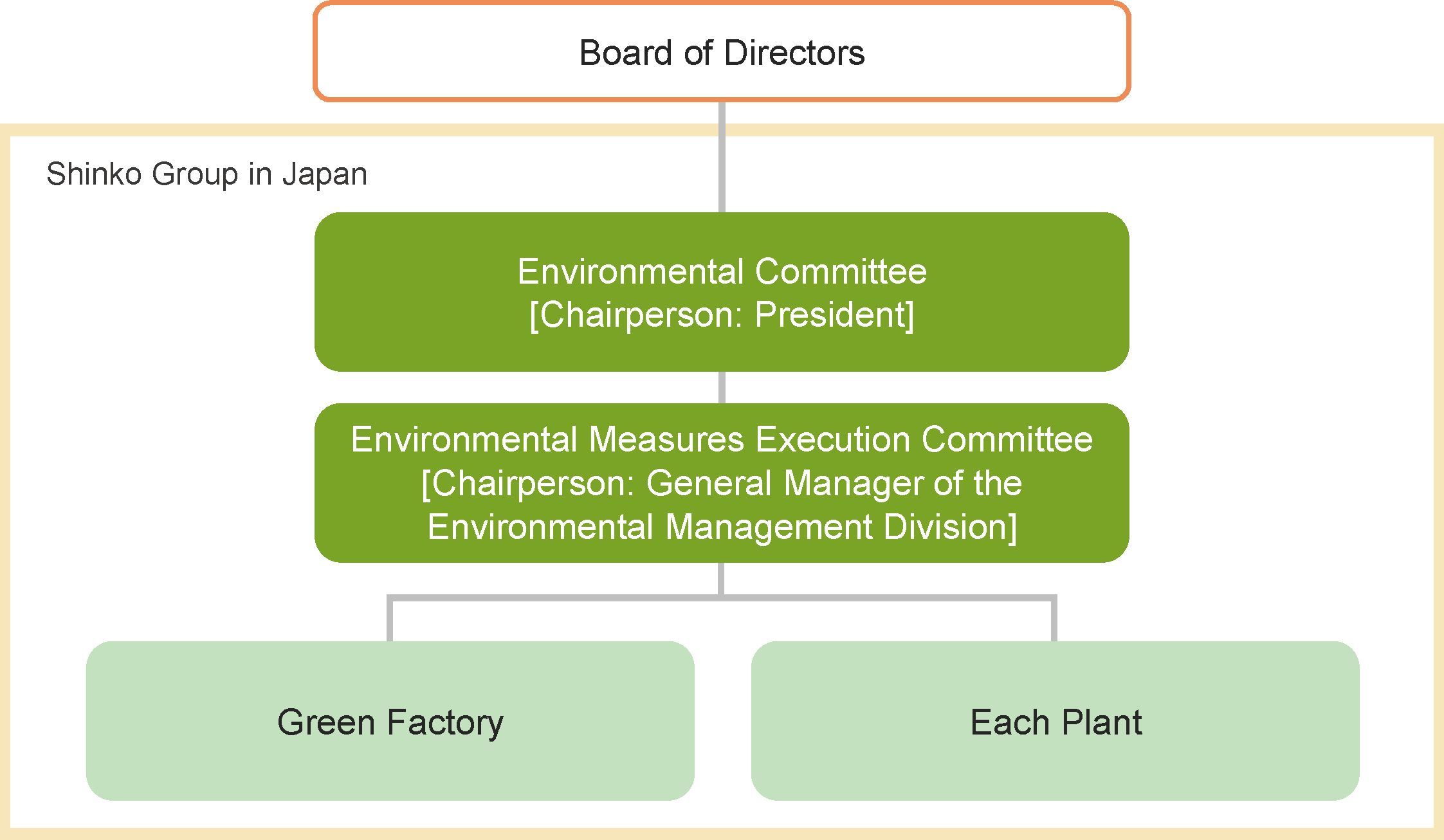
Shinko Group in Japan has established an environmental management promotion system based on its environmental management system.
To promote environmental management, we have established an Environmental Committee chaired by the Representative Director of Board, President. As the highest deliberative body for environmental measures, the Committee reviews medium- and long-term issues, formulates policies, and proposes, deliberates, and decides upon matters related to environmental management, including measures to address business risks and opportunities related to climate change, resource circulation, and living in harmony with nature.
Additionally, we have established an Environmental Measures Execution Committee as a subcommittee organization under the Environmental Committee to execute and deliberate on activities aiming at achieving environmental goals.
While strengthening governance through the establishment of this promotion system, we are promoting the maintenance and improvement of our environmental management system.
Environmental Management Promotion System
With serious deterioration of the natural environment, halting biodiversity loss and reversing this trend toward recovery is an urgent global issue. In recent years, the importance of initiatives aimed at achieving Nature positive1 has grown significantly. Global efforts to respond to various social issues are accelerating toward Nature positive, including addressing climate change, transitioning to a circular economy2, countermeasures for marine plastic pollution, and ensuring sustainable water resource use. In Japan, such efforts have also begun, starting with the Declaration of Carbon Neutrality by 2050 in 2020 to address climate change, followed by the "National Biodiversity Strategy 2023-2030" and the "Transition Strategies toward Nature Positive Economy" aimed at achieving nature positivity, as well as the Fundamental Plan for Establishing a Sound Material-Cycle Society to advance the shift toward a circular economy.
1Nature positive: The nature positive initiative seeks to arrest the loss of biodiversity and put the environment on a recovery path. Natural restoration.
2Circular economy: A circular economic system that is designed on the premise that recycling and reuse will occur starting at the stage where goods and services are produced. It maximizes the value of resources and products and minimizes resource consumption and waste generation by reducing the input and consumption of new resources as much as possible. Intended to replace the conventional economic system based on the premise of "mass production, mass consumption, and mass disposal."
Global environmental challenges are critical issues for our company as well, affecting our very survival.
Therefore, Shinko Group in Japan identify annually the effects that our business activities have on the environment, clarify the challenges and requests from stakeholder related to the environment, risks and opportunities, then determine the environmental issues to be addressed during the year, taking into consideration their importance and urgency. We reflect these environmental challenges in the activities of our environmental management system, and are deploying our initiatives to resolve them.
Shinko Group conducts environmental education for all employees in Japan at least once a year to ensure that each employee always acts in an environmentally conscious manner, both in conducting corporate activities and in living as a member of society.
We develop human resources capable of contributing to improved environmental performance. This involves education to understand the environmental impact of their work and foster awareness of environmental contributions, based on our environmental activity framework including the Environmental Policy, Environmental Vision 2050, and Environmental Targets. We also provide more specific training on environmental laws and regulations, as well as knowledge necessary for reducing environmental impact.
In FY2024, we incorporated the perspective of biodiversity—a crucial element for future environmental activities—into our training materials to educate employees.
We disseminate information on a variety of topics throughout the company on a monthly basis, including familiar seasonal themes and environmental issues surrounding our company. In June, Environment Month provides an opportunity to think about a sustainable global environment. We conduct activities such as beautifying the area around our plants and holding environmental quizzes to contribute to the community and raise environmental awareness.
Environmental Education Achievements in FY2024 [Shinko Group in Japan]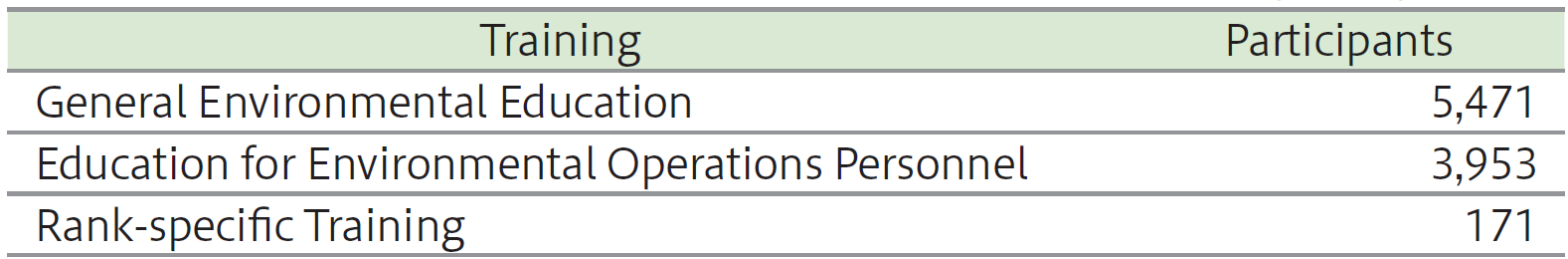
Every year Shinko Group in Japan conducts its internal environmental audit to check ISO 14001 conformance, the effectiveness of its environmental management system, and legal compliance.
When nonconformity items are revealed by audits, we analyze the causes from multiple perspectives and promptly make improvements. In addition, the results of audits, including conforming items, were shared in the entire company in an effort to continuously improve the management system.
In FY2024, we conducted audits focusing on compliance with laws and regulations and the thorough implementation of related internal rules as priority check items.
We have taken corrective action on all audit findings.
 Overseas production sites: Individual companies obtained certification
Overseas production sites: Individual companies obtained certification
| Registration office | SHINKO ELECTRIC INDUSTRIES CO., LTD. Head Office (Kohoku Plant), Wakaho Plant, Chikuma Plant, Takaoka Plant, Arai Plant, Kyogase Plant, SHINKO R&D Center, Aizu Branch Domestic Subsidiary SHINKO TECHNOSERVE CO., LTD. |
|---|---|
| Certification body | Japan Audit and Certification Organization for Environment and Quality (JACO) |
| Registration number | EC25J0011 |
| Date of registration | January 26, 2026 |
| Certification body | Bureau Veritas Certification Holding SAS – UK Branch |
|---|---|
| Registration number | MY010519 |
| Date of registration | October 18, 2000 |
| Certification body | Korean Foundation for Quality |
|---|---|
| Registration number | EAC-0642801 |
| Date of registration | July 3, 2003 |
The Shinko Group will continue to pursue environmental certification to enhance environmental performance and drive continuous improvement through ISO 14001 certification, thereby contributing to the preservation and enhancement of the global environment through environmentally conscious manufacturing.
Shinko Group in Japan strives to comply with national environmental laws and regulations as well as prefectural and city regulations, pollution prevention agreements, industry guidelines, and environmental requests from customers.
In FY2024, there was four cases of failing to observe obligation to comply with laws and regulations, and two complaints. All of them were appropriately responded to and corrected.
There were no litigation issues, fines, or penalties resulting from violations of environment-related laws and regulations, and there were no accidents with serious environmental impact.
Number of Environmental Laws and Regulations Violations or Complaints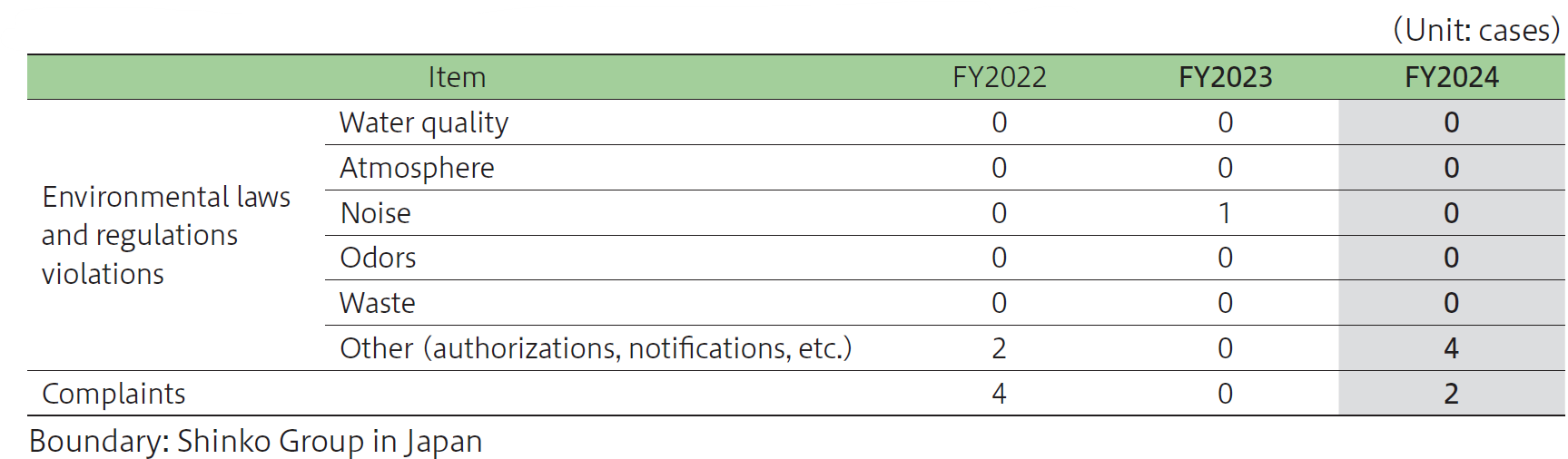
Similarly, there were no litigation issues, fines, penalties, or serious accidents at overseas production sites.