
SHINKO ELECTRIC INDUSTRIES CO., LTD.

SHINKO ELECTRIC INDUSTRIES CO., LTD.
Resources such as raw materials and water are indispensable for the manufacturing of the Shinko Group. However, there are now concerns that resources may become depleted due to loss of biodiversity and other factors. To prevent resource depletion, we recognize the importance of sustainable resource utilization and have made resource circulation one of the Shinko Group's material issues.
Therefore, we have set medium- to long-term environmental targets for "waste reduction" and "reduction of water use" to maximize effective use of resources and recycling, and are promoting activities aimed at transitioning to a circular economy and realizing a recycling-oriented society, while reducing risks to business continuity.
 Reducing Water Use
Reducing Water UseRecent years have seen the expansion of water risks such as water shortages and water pollution worldwide, driven by factors including droughts and frequent extreme weather events caused by climate change, rapid population growth, and increased water demand accompanying economic development. For the Shinko Group, which uses a large amount of water in its manufacturing processes, water resources are of high importance, and reducing water use is one of our critical issues. We are promoting the reduction of water use by advancing water recycling, water reuse, and review of water usage.
Key risks and opportunities related to water resources
The world faces various water risks1, including those already materialized such as water scarcity, water pollution, floods, droughts, and water conflicts. The Shinko Group assesses water risk, including physical risk, regulatory risk, and reputational risk, at its production sites in Japan and overseas, using the World Resources Institute's (WRI) Aqueduct, in order to understand the impact of water risks on its business activities.
Our assessment identified no production sites classified as "High" or "Extremely High" for water risk. However, we identified a production site classified as "High" for water stress2.
We have begun studying what actions are necessary based on these results. For the production site classified as "High," we have established water usage reduction targets and are actively working toward them.
1 Water risk: risks that may impact corporate activities related to water.
Includes risks related to water intake and discharge quality (pollution), as well as risks from increased regulations and reputational damage.
2 Water stress: water scarcity and deteriorating water quality causing demand for essential water to exceed supply, leading to a shortage of available water.
Assessment of Water Risk and Water Stress at Production Sites3 (FY2024)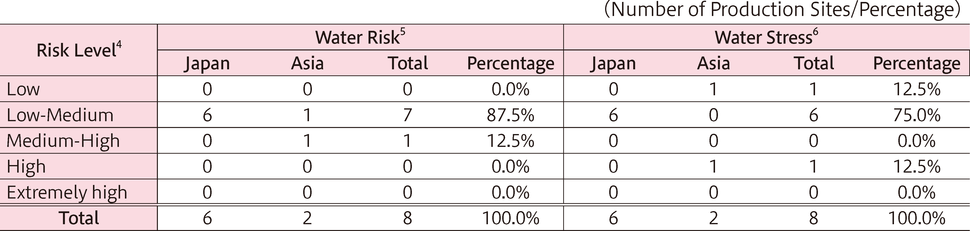
3 Production sites
[Japan]
Kohoku Plant, Wakaho Plant, Chikuma Plant, Takaoka Plant, Arai Plant and Kyogase Plant
[Asia]
KOREA SHINKO MICROELECTRONICS CO., LTD.(KSM)
SHINKO ELECTRONICS (MALAYSIA) SDN. BHD.(SEM)
4 According to Aqueduct 4.0 assessment criteria
5 Aqueduct 4.0 assessment index "Overall Water Risk"
6 Aqueduct 4.0 assessment index "Baseline Water Stress"
As shown in the pie chart, when the amount of water withdrawal by the Shinko Group is broken down by water stress levels, water withdrawal from regions classified as "Low-Medium" level or below is 99%.
However, we will continue to reduce water use and improve the water recycling rate to maximize resource circulation, taking into account that the water risk and water stress situation is constantly changing and that risks vary by watershed.
Water Withdrawal Rate According to Water Stress Level7 (Results for Production Sites)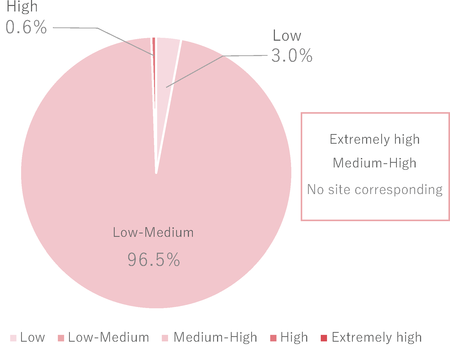
7 Water stress levels defined by aqueduct 4.0

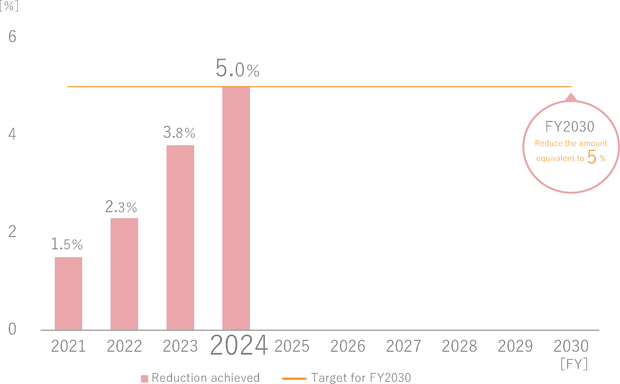
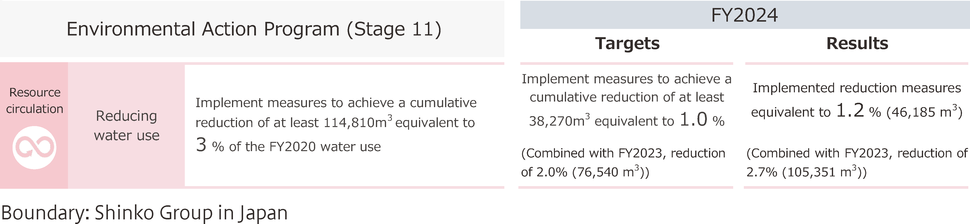
In FY2024, Shinko Group in Japan achieved the rate of reducing water use at 1.2% (46,185 m3), exceeding its target of reducing water use by at least 1.0% (38,270 m3) of the FY2020 level.
As a result, a reduction equivalent to 5.04% (192,996 m3) was achieved over the four years starting in FY2021, when activities toward the medium- to-long-term environmental targets began. This accomplishment meets the FY2030 target of the medium- to-long-term environmental targets: a reduction equivalent to 5% (191,350 m3) of the base year water usage. Therefore, we plan to review the FY2030 target value for the medium- to long-term environmental targets.
Since water usage is expected to increase from FY2025 onwards due to new line launches and increased production, we will further promote water usage reduction initiatives.
Reporting boundary: Shinko Group in Japan
Water use reduction activities are approached from both facility and manufacturing process perspectives, focusing on review of water supply, water reuse, and rationalization of production lines. The Shinko Group in Japan will continue to drive the transition to environmentally conscious processes while maintaining product quality.
By shortening cleaning times while ensuring no impact on product quality, and introducing equipment standby mode8, Shinko has reduced water usage by 5,686 m3 over the seven-month period from September 2024 to March 2025.
8 Standby mode: a setting that automatically stops water supply when products are not flowing during the cleaning process.
Since the gas used to remove the protective film (resist) from the substrate has a major greenhouse effect, Shinko decomposes it before releasing it into the atmosphere. At Wakaho Plant (Nagano City), we reduced water use by regulating the amount of water used to remove greenhouse gases via the exhaust gas treatment system (scrubber). We also made similar adjustments at Arai Plant (Myoko City, Niigata Prefecture). Combined, these measures reduced water usage by 5,648 m3 over the seven-month period from September 2024 to March 2025.
Securing a stable supply of water resources is essential for our business activities, which involve significant water usage in the manufacturing process.
Recent water intake has increased due to new plant operations and the introduction of new equipment. The Shinko Group in Japan will continue its efforts to improve recycling rates.
For example, water used for rinsing in the cleaning process is not simply discharged. Instead, it is recovered according to the degree of contamination, treated to remove impurities using the plant's water production facilities, and reused in the manufacturing process.
In this way, we will continue pushing forward with water recycling to minimize the amount of new water resources introduced.
Simultaneously, we will continuously review water input levels and advance the shift to manufacturing processes that use less water overall.
Our Water Recycling Rate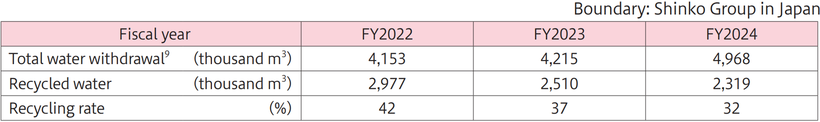
9 Total water withdrawal includes water used outside of manufacturing processes.